What Is Bitcoin Mining? A Complete Guide for Investors

Key Takeaways
- Bitcoin mining is a competition where specialized computers race to find a valid hash and earn the right to add a block to the blockchain.
- Miners receive bitcoin rewards (block subsidy plus transaction fees) for their computational work.
- Proof-of-Work transforms electricity into network security; attacking Bitcoin requires redoing all prior work.
- The block subsidy halves every four years, enforcing Bitcoin's fixed 21 million supply cap.
- Hosted mining offers investors access to industrial electricity rates and depreciation benefits without operational complexity.
Bitcoin mining is the process that creates new bitcoin and secures the entire network. Miners run specialized machines that compete to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain. The winner earns bitcoin as a reward. This mechanism transforms real-world energy into digital scarcity. For investors, understanding what is bitcoin mining separates speculation from conviction.

What Is Bitcoin Mining? Definition and Context
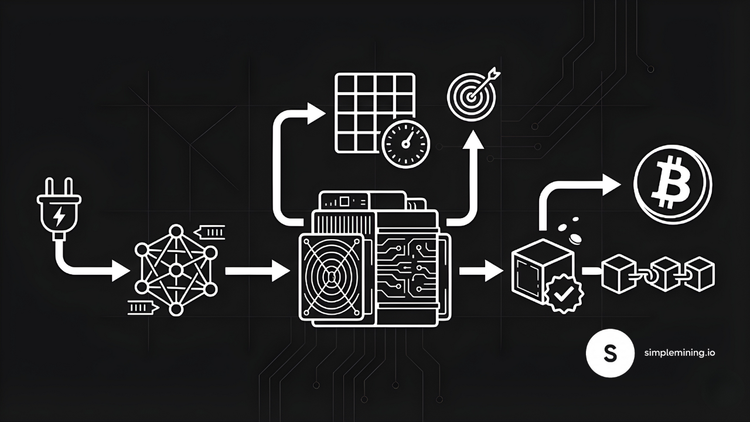
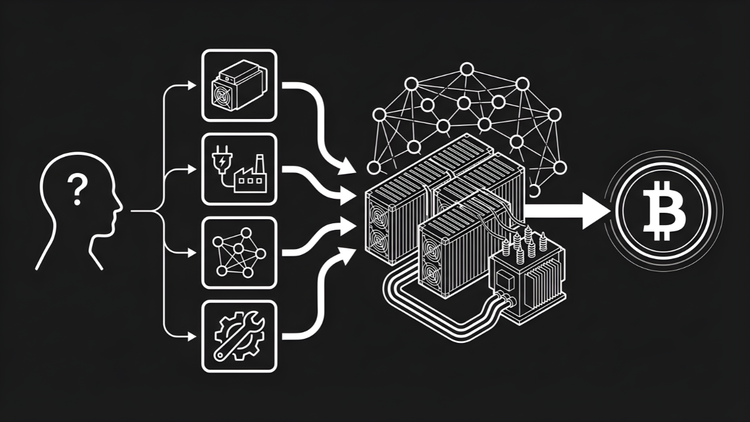
Bitcoin mining is a decentralized validation process. Miners use specialized hardware to compete for the right to add new blocks of transactions to the blockchain. Think of it like a global lottery that runs roughly every ten minutes on average.
The analogy works like this: thousands of miners each generate trillions of random guesses. The first to find a number that meets the network's criteria wins the block. This winning number serves as proof that computational work occurred.
The technical term is Proof-of-Work. Miners convert electricity into cryptographic hashes using the SHA-256 algorithm. Each hash is a guess. The network requires guesses to meet a specific difficulty target. When a miner finds a valid hash, the block gets added to the chain. This process anchors Bitcoin's security in thermodynamic reality.
How Bitcoin Mining Works: Step by Step
The mining process follows a clear sequence from transaction to confirmation.
Step 1: Transactions Enter the Mempool
When you send bitcoin, your transaction broadcasts to the network. Nodes validate the transaction and place it in the mempool. This is a waiting room for unconfirmed transactions.
Step 2: Miners Build a Block
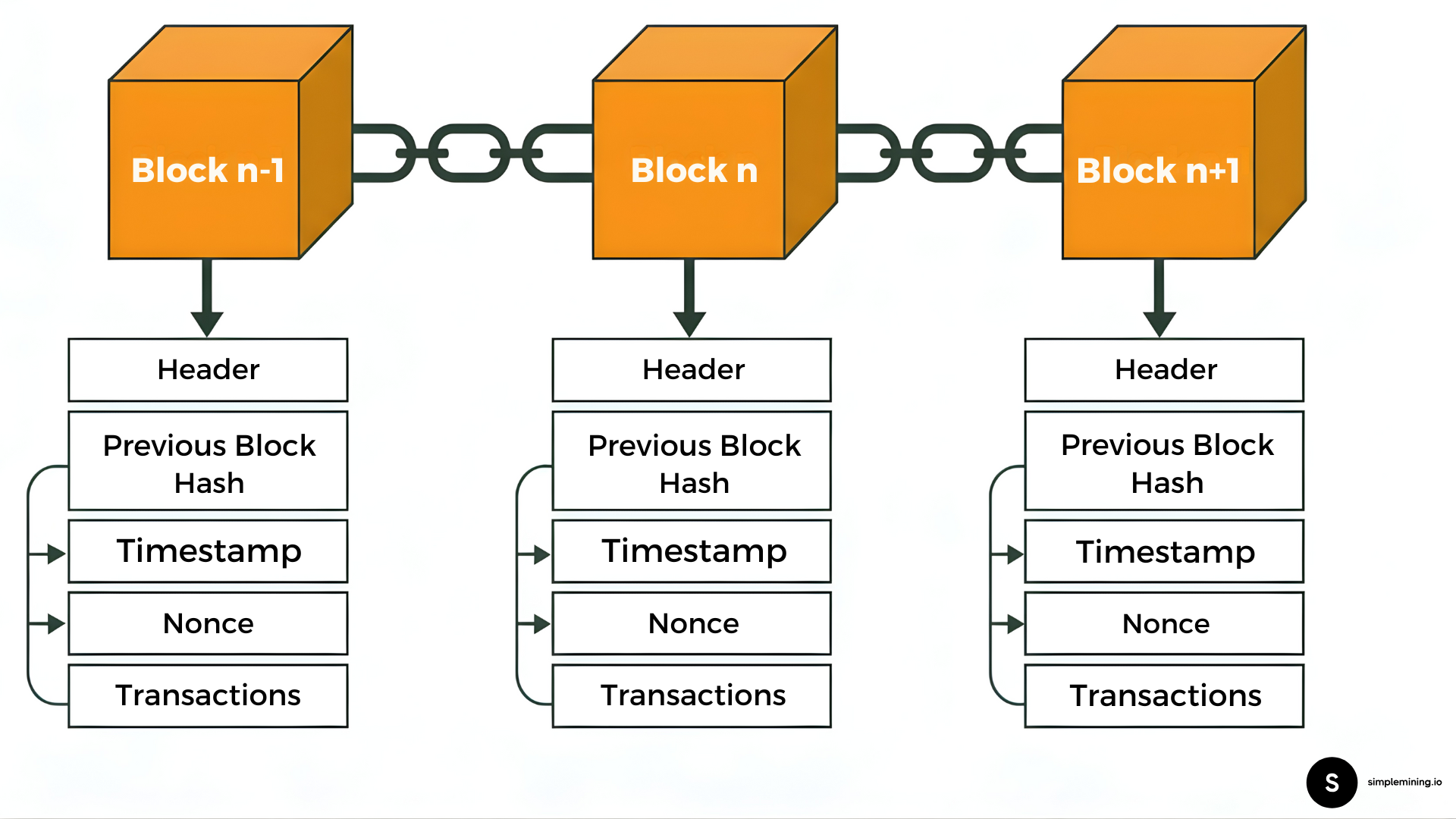
Miners select transactions from the mempool. They bundle these into a candidate block (a container for Bitcoin transactions). The block header contains a timestamp, a reference to the previous block, and a variable called the nonce.
Step 3: The Hash Competition Begins
Miners change the nonce and hash the block header. They repeat this process trillions of times per second. A modern ASIC miner produces around 200 terahashes per second. That means a single machine can make about 200 trillion guesses every second.
Step 4: A Miner Finds a Valid Hash
One miner finds a nonce that produces a hash below the difficulty target. The difficulty target adjusts every 2,016 blocks to keep block times stable. The odds resemble finding one specific grain of sand across thousands of Earth-like planets. With global hashrate pooled together, miners find this number about every ten minutes on average.
Step 5: The Block Gets Confirmed
The winning miner broadcasts the new block. Other nodes verify the work and add the block to their copy of the blockchain. The transactions inside now carry one confirmation. Each subsequent block adds another layer of security.
Example with Numbers:
For example, suppose the network hashrate totals around 800 exahashes per second. A single S21 Pro miner produces 234 terahashes per second. Your share of the network equals about 0.000029%. Solo mining means waiting years between block finds. This math explains why pools exist.
Why Investors Care About Bitcoin Mining
Bitcoin mining determines the security and issuance schedule of the asset you own. Understanding this process changes how you evaluate risk.
Security Through Energy
An attacker wanting to reverse transactions must redo the computational work of all subsequent blocks. This requires controlling more than half of global hashrate. Such an attack would require billions of dollars in hardware and electricity.
Predictable Supply
Mining is the sole mechanism for new bitcoin issuance. The block subsidy halves every 210,000 blocks. This occurs about every four years. After the April 2024 halving, miners receive 3.125 BTC per block. This schedule continues until around 2140, when the block subsidy reaches zero. No central bank can print more bitcoin. No committee votes on supply changes.
Revenue Fundamentals
Miner revenue comes from two sources: the block subsidy and transaction fees. Revenue per unit of hashrate is called hashprice. This metric tracks the dollars a miner earns per terahash per day. Hashprice fluctuates with bitcoin price, network difficulty, and fee market activity.
What Can Go Wrong
Hashrate can drop if mining becomes unprofitable. A sustained price crash or regulatory crackdown could reduce network security. However, difficulty adjusts downward when hashrate leaves. This makes mining easier and restores equilibrium. The protocol self-corrects.
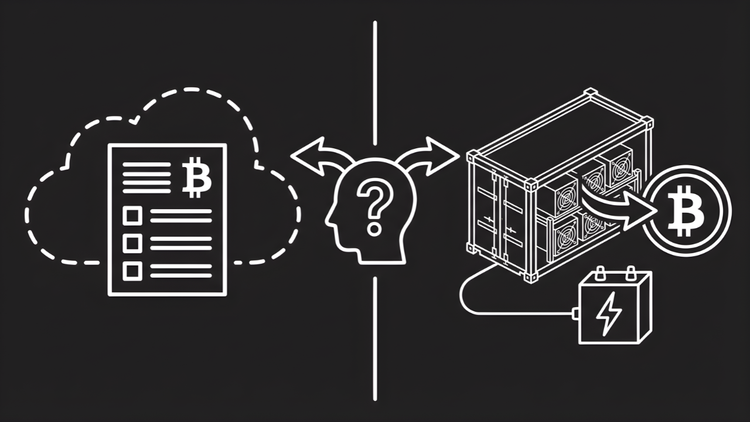
Decision Framework: Should You Mine Bitcoin?
Use this framework to evaluate whether mining fits your situation.
If you want direct bitcoin exposure with tax advantages:
Mining can offer depreciation benefits on hardware, depending on your structure and jurisdiction. Section 179 deductions can accelerate write-offs. Mined bitcoin receives cost basis at fair market value when earned. Consult a CPA familiar with digital assets. Tax treatment is highly situation-dependent.
If you want to accumulate bitcoin regardless of price:
Mining produces bitcoin through operations. You receive bitcoin whether the price rises or falls. This strategy favors long-term holders who want steady accumulation.
If you want to minimize counterparty risk:
Mining hardware sits in a physical location. You own the asset producing bitcoin. No exchange holds your keys. Your exposure exists outside the traditional financial system.
If you cannot tolerate operational complexity:
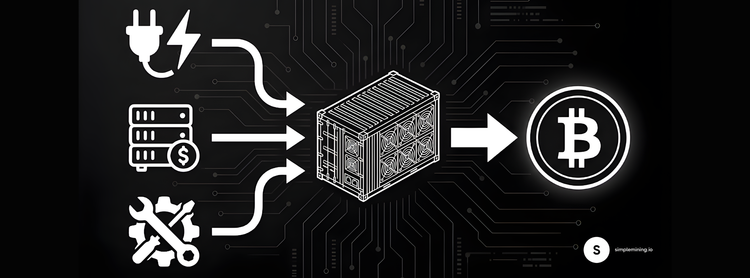
Mining involves hardware, electricity, and maintenance. Hosted mining removes most complexity. You own the machine while the facility handles operations.
If your electricity cost exceeds $0.08/kWh:
Home mining at retail electricity rates often proves unprofitable. Industrial facilities often secure rates between about $0.03 and $0.08 per kWh. Hosted mining provides access to these economics.
Compare Your Options: Mining vs. Buying vs. ETFs
Each path to bitcoin ownership carries different trade-offs.
| Factor | Direct Mining | Spot Purchase | Bitcoin ETF |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acquisition Cost | Variable (can be below spot) | Market price + fees | Market price + expense ratio |
| Tax Treatment | Depreciation + expense deductions | Capital gains only | Capital gains only |
| Custody | Self-custody or hosted | Self-custody or exchange | Fund custody |
| Cash Flow | Daily/weekly payouts | None | None |
| Operational Complexity | Low (hosted) to High (self-run) | Low | Low |
| Counterparty Risk | Pool and host dependent | Exchange dependent | Fund and custodian dependent |
| Ongoing Fees | Hosting + electricity | None after purchase | Expense ratio (0.2–0.9% annual) |
Mining wins when you secure cheap electricity and maintain high uptime. Spot purchases win when you want simple exposure with no ongoing management. ETFs win when you need exposure inside a standard brokerage or retirement account.
For investors seeking tax-advantaged accumulation, mining offers depreciation benefits unavailable through direct purchase or ETFs. The key variables are electricity cost and hardware efficiency. Control those inputs and mining can become a reliable long-term accumulation engine.
The Simple Mining Angle
Simple Mining exists to make Bitcoin mining accessible without sacrificing returns or introducing friction.
On-Site Repairs:
Our facility employs technicians who service machines in-house. A failed hashboard gets fixed within days. You avoid shipping delays and third-party repair costs.
Precision Billing:
We bill based on actual power consumption. You pay for what your machines use. No inflated estimates or hidden fees.
Renewable Energy Mix:
Our facility sources a significant share of its power from renewable sources. This includes hydro and wind. A lower carbon footprint aligns with responsible capital allocation.
Uptime and Reliability:
Professional operations mean consistent hashrate. Our infrastructure includes redundant power and cooling systems. Maximized uptime translates to maximized revenue.
7-Day Trial:
New clients can test a miner for seven days without commitment. See real performance data before you deploy capital.
Transparent Operations:
We provide dashboards showing your miner's output. You track hashrate and earnings in real time.
For more on mining economics, read our guide on hashrate fundamentals and mining profitability factors.
Conclusion
Bitcoin mining converts electricity into the most secure monetary network in history. It enforces scarcity through Proof-of-Work and produces new bitcoin on a fixed schedule. Investors who understand what is bitcoin mining gain clarity on what makes this asset different from every alternative.
Mining is the furnace that forges sound money.
Want to see real mining economics in action? Start a 7-day free trial and run your own ASIC with no commitment.