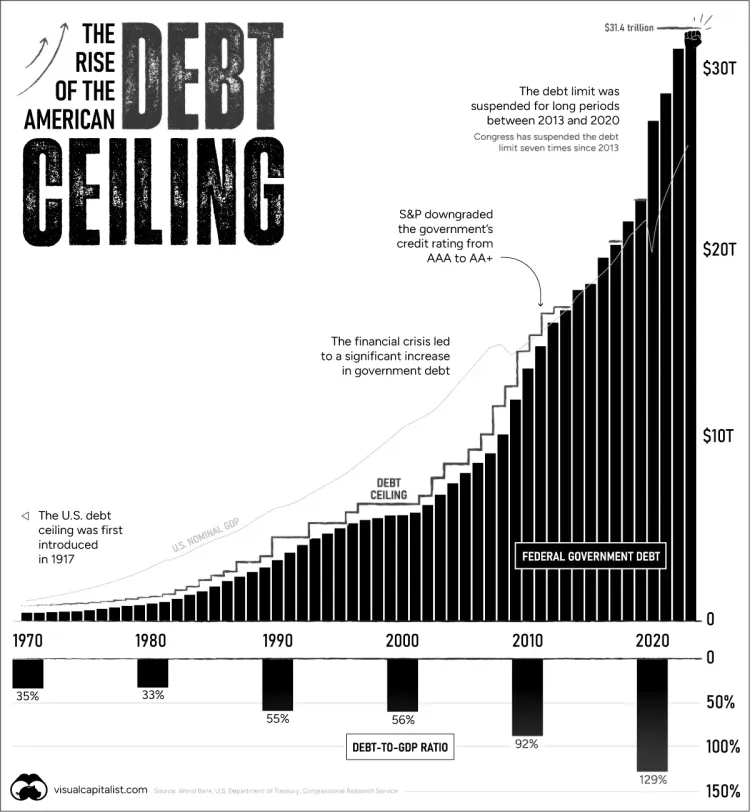
What is a Bitcoin Node?
A node is the rule keeper of the Bitcoin network, maintaining its security, transparency, and distributed nature.
A Bitcoin node is a computer that participates in the Bitcoin network by running the Bitcoin Core software.

Different types of nodes exist, but they all contribute to verifying and achieving consensus for transactions across the network.
Why Are Bitcoin Nodes Important?
Understanding Bitcoin nodes is important because they form the foundation of the Bitcoin network. Here are several reasons why nodes are important:
- Decentralization: Bitcoin's strength lies in its distributed nature of software. Nodes help achieve this by ensuring no single entity controls the network. Each node acts as a referee to verify transactions, ensuring that all participants follow the same rules.
- Security: Nodes contribute to the network's security by validating transactions and blocks. This prevents fraudulent activities such as double-spending, where someone might try to spend the same Bitcoin twice.
- Transparency and Trust: By running a node, you can verify transactions yourself rather than relying on third parties. This transparency fosters trust in the system, as anyone can audit transactions and verify with a node.
- Support the Network: Nodes propagate transactions and blocks across the network, ensuring they reach other nodes and miners. This propagation is needed to support the network's efficiency and reliability.
How Does a Bitcoin Node Work?
A Bitcoin node works by performing several key functions:
- Downloading the Blockchain: When you run a full node, your computer downloads a copy of the entire Bitcoin blockchain, which contains every transaction ever made. This can take up a significant amount of storage, currently over 400 GB.
- Verifying Transactions and Blocks: Nodes check the validity of transactions and blocks against the consensus rules of the Bitcoin Core protocol. They ensure that transactions are properly signed and that blocks are mined according to the network's difficulty requirements.
- Propagating Transactions and Blocks: After verifying, nodes spread transactions and blocks to other nodes, helping to keep the network updated and synchronized.
- Maintaining a Copy of the Blockchain: Nodes store a copy of the blockchain, ensuring the historical record of transactions is preserved and available for reference.
What Can You Do with This Information?
Knowing what a Bitcoin node is and why it's important can empower you in several ways:
- Run Your Own Node: By running a node, you can directly contribute to the Bitcoin network's security and decentralization. It also allows you to verify transactions independently, enhancing your privacy and control over your Bitcoin usage.
- Better Understanding: Understanding nodes helps you grasp Bitcoin's fundamental workings. This knowledge can be valuable if you want to build confidence as an invested network participant.
- Promote Decentralization: Encouraging others to run nodes can help maintain and strengthen Bitcoin's decentralized nature. This can be particularly important in preserving the principles of transparency, security, and trust that Bitcoin was founded on.
A Bitcoin node is a computer running the Bitcoin software, a network pillar that provides decentralization, security, and transparency.
By understanding nodes and how they work, you can appreciate the Bitcoin network's technological innovation and even participate in maintaining its integrity.
Running your own node increases your sovereignty as an individual and maintains the broader Bitcoin ecosystem.