What is a Bitcoin Halving?

If you own or mine Bitcoin, you've likely heard of the "Bitcoin Halving." While it might sound mysterious, we're here to make it simple. By the end of this, you'll easily explain it to your friends and family.
What Bitcoin Halving is NOT:
- It does NOT cut the number of bitcoins in the market in half.
- It does NOT halve the price of a bitcoin.
- It does NOT reduce Bitcoin transactions by half.
What Does the Bitcoin Halving Do?
The halving reduces the amount of bitcoin a “miner” can earn for producing a new block.
Understanding Bitcoin Mining:
Bitcoin miners generate bitcoins by solving complex math problems outlined in the Bitcoin protocol. The protocol is a rulebook for how Bitcoin operates.
Miners ensure that no one can send more bitcoin than they own by adding new blocks to the blockchain, a digital ledger recording every transaction. Mining is energy-intensive and challenging, similar to mining for gold.
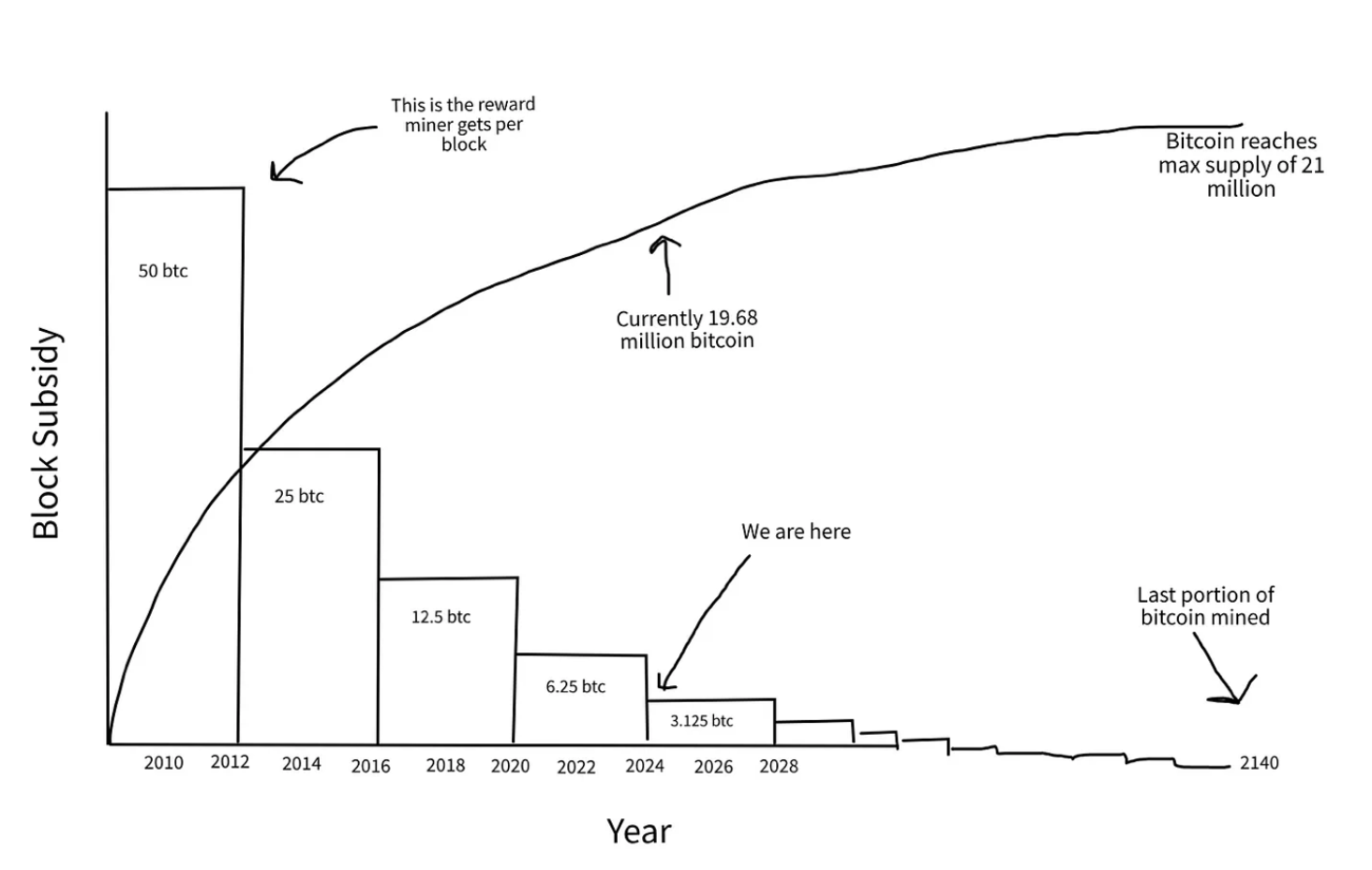
Miners compete to add the next block to the chain. The first one to solve the problem gets a reward, which is a combination of the block subsidy and transaction fees. The block subsidy is the reward defined in the Bitcoin code, which changes every four years.
The History of Bitcoin Halving:
- January 3, 2009: The first block (Genesis Block) was mined with a reward of 50 bitcoins.
- November 28, 2012: The reward was halved to 25 bitcoins.
- July 9, 2016: The reward was halved to 12.5 bitcoins.
- May 11, 2020: The reward was halved to 6.25 bitcoins.
- April 19, 2024: The reward was halved to 3.125 bitcoins.
Bitcoin’s Fixed Supply:
Bitcoin’s code caps the total supply at 21 million coins. Changing this would be next to impossible because you would need to convince everyone else to use the software with your changed rule — like changing the rules of chess.
Current State of Bitcoin:
- At the time of writing, 19.71 million bitcoins have been mined.
- The remaining 1.32 million will be mined according to the schedule until around 2140.
Incentives for Miners After 2140:
After the last bitcoin is mined, miners will earn revenue from transaction fees. As more people use Bitcoin, these fees will rise, ensuring miners remain incentivized to maintain the network.
Bitcoin vs. Fiat Currency:
Bitcoin is deflationary, meaning fewer new bitcoins are introduced over time. Unlike fiat currency (like the US dollar), which can be printed in unlimited amounts, Bitcoin has a fixed supply. It is a programmed system enforced by math, not a political system enforced by manipulation.
The Importance of the Halving:
The Bitcoin halving is important because it ensures Bitcoin’s scarcity, contributing to its value. It's part of what makes Bitcoin a revolutionary technology compared to traditional, inflation-prone currencies.
In summary, the Bitcoin halving is a pivotal event in the Bitcoin network. It reduces the reward for mining and ensures the currency's deflationary nature.
Understanding it sheds light on what makes Bitcoin unique and the brilliance of the technology.